SIMSLab
Modeling and Analysis of Water Pipe Failure: Investigate Causes, Find Solutions, and Develop Potential Strategies, Polices, and Regulations
Abstract / Brief Description
Modeling and Analysis of Water Pipe Failure: Investigate Causes, Find Solutions, and Develop Potential Strategies, Polices, and Regulations
Funding Scheme: Innovation and Technology Fund and Water Supplies Department of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (ITS/033/20FP)
Funding Amount: $7,599,200.00
Principal Investigator: Ir. Prof. ZAYED Tarek
Project Scope
Condition assessment of water pipes in Hong Kong relies primarily on reactive maintenance after failures occur and limited historical data analysis. However, these methods fail to predict failures proactively, lacking standard procedures for comprehensive
structural assessment and neglecting critical operational and environmental conditions. Previous research showed that existing models inadequately address root causes of leakage and burst failures, while the combined effects of internal pressure cycling and
external loads from ground movement remain poorly understood. To overcome these limitations, this research integrated four advanced analytical approaches in the investigation process.
- Material Science and Corrosion Analysis for examining failed pipe samples and epoxy lining deterioration.
- Geotechnical and Soil Chemistry Testing to assess environmental impacts (pH, chloride, sulfate, resistivity).
- Mechanical and Structural Testing under combined loading conditions.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for predictive modeling using historical data.
Advanced algorithms were employed to analyze the combined data from these multidisciplinary approaches, resulting in a holistic pipe diagnosis system designed to identify failure mechanisms and predict critical deterioration. The project had the following objectives:
- Design innovative deterioration models for water pipes using AI techniques and historical data;
- Identify and study failure causes specific to Hong Kong's environment through extensive laboratory and analytical methods; and
- Develop a Smart Pipe Diagnosis System integrating condition assessment, probability of failure, and time-to-failure predictions.
Technology Deployments
Project Findings
- A performance rating model called Condition Index (CI) has been proposed and AI techniques were used to develop deterioration models for water pipes in Hong Kong.
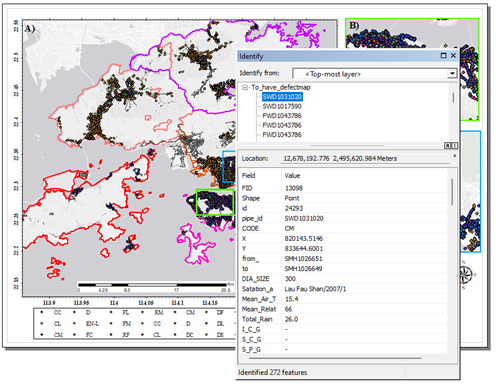
- Root factors causing water pipe failure were scrutinized and an engineering database was developed to store the collected data using GIS as a platform.
- Damage and delamination of epoxy lining have been proven to the main cause of internal corrosion of steel saltwater pipes.
- pH level, resistivity, sulphate ion concentration and chloride ion concentration are the most critical parameters for the external corrosion of iron-based pipes.
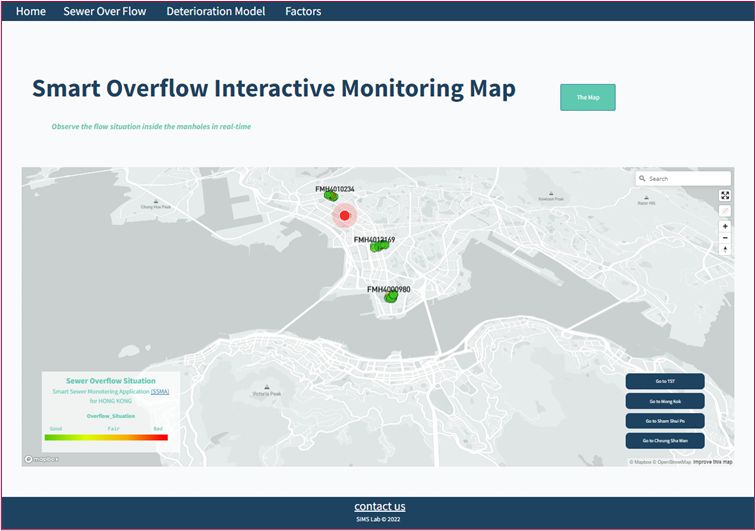
- A prototype of an automatic tool, i.e., smart pipe diagnosis system (SPDS) has been developed.
Pipe Failures
SIMSLab